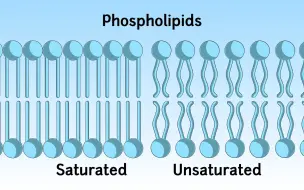
7. DNA 损伤会阻碍细胞周期
TIP! Right-click and select "Save link as..." to download.
| VIDEOS | |||
| MP4 | N/A | 480P | Download |
| MP4 | N/A | 360P | Download |
| AUDIO | |||
| MP4 | N/A | mp4a.40.2 | Download |
| MP4 | N/A | mp4a.40.2 | Download |
| MP4 | N/A | mp4a.40.2 | Download |
| THUMBNAILS | |||

|
JPEG | Origin Image | Download |
At various checkpoints during the cell cycle, multiple enzymes probe the DNA for damage. To maintain the integrity of the genome, only intact, undamaged DNA is allowed to pass through this cycle, and on to the next generation. If DNA damage is detected, the cell cycle pauses until this is repaired.
During DNA replication in the G1 phase, helicase unwinds the DNA, and DNA polymerase synthesizes a new strand from the template - creating a Y-shaped structure called a replication fork. Damaged DNA stalls the replication fork, causing it to become unstable, and the helicase and polymerase to uncouple from the DNA.
To prevent the damaged single-stranded DNA from reannealing, replication protein A or RPA, coats the single-stranded DNA at the stalled replication fork. This complex is then detected by the ATR protein, also known as ataxia or Rad-3 related protein.
If the damaged DNA is not a single mutation but a full double strand break, a protein complex called MRN is recruited at the site, which bridges the two damaged ends of the DNA and provides a platform for binding of the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, or ATM protein.
Both ATM and ATR are kinases, which means they catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from phosphate-donating molecules such as NTPs, to specific substrates.
ATR and ATM phosphorylate the downstream kinases Chk1 and Chk2, respectively. Chk1 and Chk2 phosphorylate CDC25, which prevents it from accepting further phosphates from CDK1. CDK1 is the regulator of the cell cycle, and as long as it remains inactive, this prevents the cell from progressing to the S phase.
Another target of ATR and ATM phosphorylation is the transcription activator protein p53. Phosphorylated p53 can directly bind to DNA, which stimulates another gene to produce a protein called p21. p21 inhibits the cell division-stimulating protein cdk2, preventing the cell from progressing to the next stage of cell division.
During DNA replication in the G1 phase, helicase unwinds the DNA, and DNA polymerase synthesizes a new strand from the template - creating a Y-shaped structure called a replication fork. Damaged DNA stalls the replication fork, causing it to become unstable, and the helicase and polymerase to uncouple from the DNA.
To prevent the damaged single-stranded DNA from reannealing, replication protein A or RPA, coats the single-stranded DNA at the stalled replication fork. This complex is then detected by the ATR protein, also known as ataxia or Rad-3 related protein.
If the damaged DNA is not a single mutation but a full double strand break, a protein complex called MRN is recruited at the site, which bridges the two damaged ends of the DNA and provides a platform for binding of the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, or ATM protein.
Both ATM and ATR are kinases, which means they catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from phosphate-donating molecules such as NTPs, to specific substrates.
ATR and ATM phosphorylate the downstream kinases Chk1 and Chk2, respectively. Chk1 and Chk2 phosphorylate CDC25, which prevents it from accepting further phosphates from CDK1. CDK1 is the regulator of the cell cycle, and as long as it remains inactive, this prevents the cell from progressing to the S phase.
Another target of ATR and ATM phosphorylation is the transcription activator protein p53. Phosphorylated p53 can directly bind to DNA, which stimulates another gene to produce a protein called p21. p21 inhibits the cell division-stimulating protein cdk2, preventing the cell from progressing to the next stage of cell division.



![Download Video: 全200集【儿童科普动画片]【生活中的化学】~一天五分钟轻松涨知识,孩子一看就感兴趣的物理小知识适合3-15岁朋友观看](https://i2.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/fe7d1f79fd0cb4b23192908e883fe93c1038347d.png@336w_190h_!web-video-rcmd-cover.webp)